Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Chatbot for Multilingual Healthcare Environment Using Bio-BERT
Authors: D Kavya, D Kiran Kumar, Divya Anjali M, Ganesh A P
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2025.66243
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Access to clear health information is crucial, many people in rural and underserved areas encounter challenges such as complex medical terminology, language barriers, and a shortage of healthcare providers. These obstacles can result in confusion, delays, and poor health outcomes. A multilingual AI chatbot can simplify medical information, provide real-time assistance, and offer guidance in the user\'s preferred language. This solution can enhance access to healthcare, bridge existing gaps, and empower individuals to make informed health choices.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Healthcare information accessibility is a crucial instrument of empowerment, enabling individuals to make informed health decisions. However, many people face significant challenges in understanding medical reports and symptoms, particularly in rural and underserved communities that lack access to proper healthcare facilities. Language barriers and limited access to service providers, combined with low medical literacy, further complicate this issue. Consequently, there exists a substantial gap in health accessibility, leaving many individuals unable to comprehend important health information or to take timely medical action. Despite significant advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP), a large portion of the population remains excluded from these benefits. Medical reports are often filled with technical jargon that can be difficult for those unfamiliar with medical terminology to understand. Additionally, the wealth of information available online regarding symptoms can be unreliable, overwhelming, and frequently misleading. The dominance of major world languages in medical reports and tools further restricts access for speakers of global dialects and local languages, making it difficult for them to engage with the information. To address these challenges, we propose an innovative solution that leverages AI-powered summarization of medical reports through a multilingual chatbot.
This system will allow users to upload health reports in PDF format, which it will then process to generate simplified, easy-to-understand summaries of diagnoses and findings. The chatbot will also enable users to ask questions related to their symptoms, receive accurate information about diseases and their causes, and interact in their preferred language, thereby promoting accessibility and inclusivity. We aim to bridge the complex health sector information gap for end-users by employing advanced NLP models, such as Bio-BERT. This initiative will enhance individuals' health decisions while facilitating a more equitable distribution of healthcare resources. Additionally, it will encourage preventive care by providing timely advice from healthcare professionals regarding their health. In the long term, this project aims to transform access to and understanding of healthcare information. Improved health literacy can lead to better patient outcomes and a more equitable healthcare system. By prioritizing inclusivity and accessibility, this initiative aspires to create a world where everyone can understand their health and take charge of their well-being effectively
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
- Mohammad Abu Tareq Rony, Mohammad Shariful Islam, Tipu Sultan, Samah Alshathri, and Walid El-Shafai present MediGPT, an advanced framework that utilizes ChatGPT to classify medical texts. The system emphasizes the importance of prompt engineering, where carefully designed prompts guide ChatGPT to accurately categorize medical statements and minimize unnecessary details. By employing an autoregressive inference mechanism, MediGPT progressively builds responses based on learned language patterns, enabling it to handle complex medical texts. The framework optimizes cross- linguistic text classification through various prompt configurations, outperforming traditional machine-learning models and pre-trained language models. The results demonstrate MediGPT’s potential to improve medical informatics, providing healthcare professionals with an efficient and reliable decision-making and data management tool.
- Tom Nadarzynski, Oliver Miles, and Damien Ridge. This study investigates the acceptability of AI-led health chatbots in healthcare. Using a mixed-methods approach, the research involved 29 interviews and a survey of 216 participants. Key findings include general awareness but limited understanding of chatbots, concerns about accuracy, security, and empathy, and recognition of benefits like convenience and anonymity for sensitive issues. The survey showed moderate acceptability (67%), positively correlated with trust and perceived utility. The study concludes that though many users are willing to engage with health chatbots, concerns regarding AI technology hinder engagement. Designers should adopt user-centered approaches to address the concerns and enhance trust.
- Akash Goel, Satyam, Shubham Sharma. This research aims to design an AI-based healthcare chatbot that assists in determining a patient's health and provides basic information for minor health issues before consulting a doctor. The primary goal is to reduce healthcare costs and increase medical knowledge by offering an alternative for non-critical health concerns. The chatbot uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to interact with users, retrieve queries from a medical database, and provide responses based on the available information. By leveraging these technologies, the chatbot serves as a preliminary resource for users, helping them gain insights into their health and reducing unnecessary doctor visits for minor issues. This approach aims to improve healthcare accessibility while offering a cost-effective solution for basic medical guidance.
- Kidwai, Bushra R K, Nadesh. This research aims to design an AI-based healthcare chatbot that helps diagnose minor health issues by analyzing symptoms and providing preliminary diagnoses. Using natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML), the chatbot interacts with users and classifies symptoms to offer medical insights. The system is trained on labeled data, such as fever and headache indicating a cold, to provide accurate responses. This approach reduces healthcare costs by offering immediate, cost-effective guidance before consulting a doctor. The chatbot enhances accessibility to basic medical advice, improving healthcare efficiency and reducing unnecessary doctor visits.
- K Jayashree, Monika K A, Preetha R, Piraisoodan S P.This research aims to design an AI-based healthcare chatbot that helps users predict and diagnose potential illnesses based on the symptoms they provide. The chatbot engages in a text-based conversation with users, collecting information about their health concerns and predicting possible diseases. Unlike existing medical chatbots that only connect users to medical forums, this system offers personalized symptom analysis and suggests potential diagnoses. If a serious condition is predicted, the chatbot provides relevant doctor contact details for further consultation. This approach aims to improve the accuracy and efficiency of initial health assessments, empowering users to better understand their health and seek timely medical attention.
- M.S Bennet Praba, Sagari Sen, Chailshi Chauhan, Divya Singh. This research focuses on designing an NLP-based healthcare chatbot to help individuals overcome communication barriers about health concerns. The chatbot uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand user input and provide accurate responses. By analyzing user queries through morphological analysis, the system identifies intent and context, minimizing confusion. The goal is to offer an interactive platform for discussing sensitive health issues without embarrassment. This system improves accessibility to healthcare information while ensuring a lightweight, cost-effective solution. It empowers users to address health concerns privately and confidently.
- Akshay Mendon, Megha Rani Patil, Yash Gupta, Vatsal Kadakia and Hash Doshi. This research aims to develop an AI-based healthcare chatbot to help patients analyze their symptoms and receive basic medical insights. Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP), the chatbot simulates human-like conversations, offering personalized responses. It provides information about diseases based on symptoms and answers questions about medications and general healthcare. The system aims to ease the burden on healthcare services, especially during crises like the pandemic. By offering initial guidance, the chatbot reduces healthcare costs and improves accessibility to medical knowledge.
- Shahadat Uddin, Arif Khan, Md Ekramul Hossian and Mohammad Ali Moni. This research explores the use of supervised machine learning algorithms for disease prediction by comparing their performance and identifying trends in their application. Algorithms like support vector machines, logistic regression, and artificial neural networks use labeled datasets to classify patients into risk categories, enhancing predictive accuracy. The study reviews various research works that employ more than one supervised algorithm for disease prediction, ensuring unbiased comparisons. With the increasing availability of electronic health records, machine learning provides robust alternatives to traditional statistical methods, reducing biases and improving healthcare quality. This study highlights the advantages and limitations of various algorithms, offering insights to guide future research in predictive disease modeling.
- Gopi Battineni, Nalini Chintalapudi, and Francesco Amenta This research introduces an AI-based chatbot designed to assist in managing the challenges posed by the Coronavirus (nCOV-19) pandemic, particularly in remote areas. The chatbot offers preventive measures, virus updates, and psychological support, helping mitigate the impact of isolation and fear. It performs diagnostic evaluations, suggests immediate actions, and assesses infection severity. In cases of serious symptoms, the chatbot connects patients with registered doctors for further consultation. This virtual assistant aims to enhance healthcare accessibility and support during the pandemic by reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
- Srinivasa Rao Damaraland, N Chandana, T Rajeshwar Rao, A Lahari, B Aparna. This research focuses on developing an AI- powered healthcare system with a chatbot to enhance user interaction and support. The chatbot uses a real-time knowledge base in JSON format to process and respond to queries in text and speech. It diagnoses symptoms, predicts health issues, and recommends doctors or immediate actions. Additionally, it offers navigation links based on user needs and provides diagnostic information. This system improves healthcare accessibility and streamlines user experience.
III. PROBLEM DEFINITION
Understanding medical reports and accessing accurate health information is inherently complex, further complicated by the use of technical jargon, language barriers, and limited access to healthcare professionals. Individuals, especially those without medical expertise, often struggle to interpret these reports accurately, relying on limited resources that can vary widely in credibility. The consequences include delays in understanding diagnoses, misinformed health decisions, and increased stress and anxiety.
Existing tools for medical information, such as online platforms and apps, suffer from significant limitations. These systems often provide generic explanations based on static datasets, which fail to account for individual linguistic needs, cultural contexts, or real-time scenarios. They also lack actionable features, such as offering personalized guidance based on specific symptoms or medical reports.
This project aims to address these challenges by developing a multilingual AI-powered system that:
- Simplifies complex medical terminology using advanced natural language processing techniques.
- Provides real-time explanations and guidance in the user’s preferred language.
- Ensures accuracy and credibility by integrating with trusted medical databases.
- Offers tailored recommendations based on individual reports and symptoms, creating a personalized experience.
By integrating technology with health literacy and cultural sensitivity, this system seeks to revolutionize healthcare access, empowering individuals to make informed decisions, reduce anxiety, and bridge critical gaps in health communication.
IV. MODULE DESCRIPTION
The proposed system is built using multiple modules:
A. Report Upload Module
This module lets users upload medical reports in PDF format via a web interface, ensuring seamless input for further processing. It validates file types and sizes for security and initiates preprocessing for downstream tasks.
B. PDF Extraction Module
Extracts plain text from uploaded PDF files using PyPDF2, handling multi-page documents and ensuring clean text formatting. It also detects and removes non-text elements like images or annotations for better processing.
C. Summary Generation Module:
Generates concise summaries of extracted text using a fine-tuned Bio-BERT model for domain-specific abstractive summarization. It processes input text through tokenization and embeddings for natural language output.
D. Query Answering Module
Allows users to ask context-specific questions about their medical reports, leveraging Bio-BERT for accurate responses. It supports various query types, such as symptoms or diagnosis-related questions, ensuring high accuracy.
E. Database Management Module
Stores uploaded reports, generated summaries, and user interactions in a Firebase database. It enables retrieval of past summaries and answers, ensuring seamless access for logged-in users.
F. User Interface Module
Provides a responsive web interface for uploading reports, viewing summaries, and interacting with query responses. It maintains a session-based, chat-like interaction log for a user-friendly experience.
V. RESULTS AND EVALUATION
The System achieved over 90% accuracy in text extraction for standard PDFs, with a slight drop for low-quality scans or handwritten formats. The Bio-BERT-based summarization model retained critical medical terms, matching manually created summaries effectively. The question-answering module provided accurate, context-specific responses, while multilingual support via Google Translate ensured accessibility with preserved medical terminology across languages. These results highlight the system's robustness and efficiency.
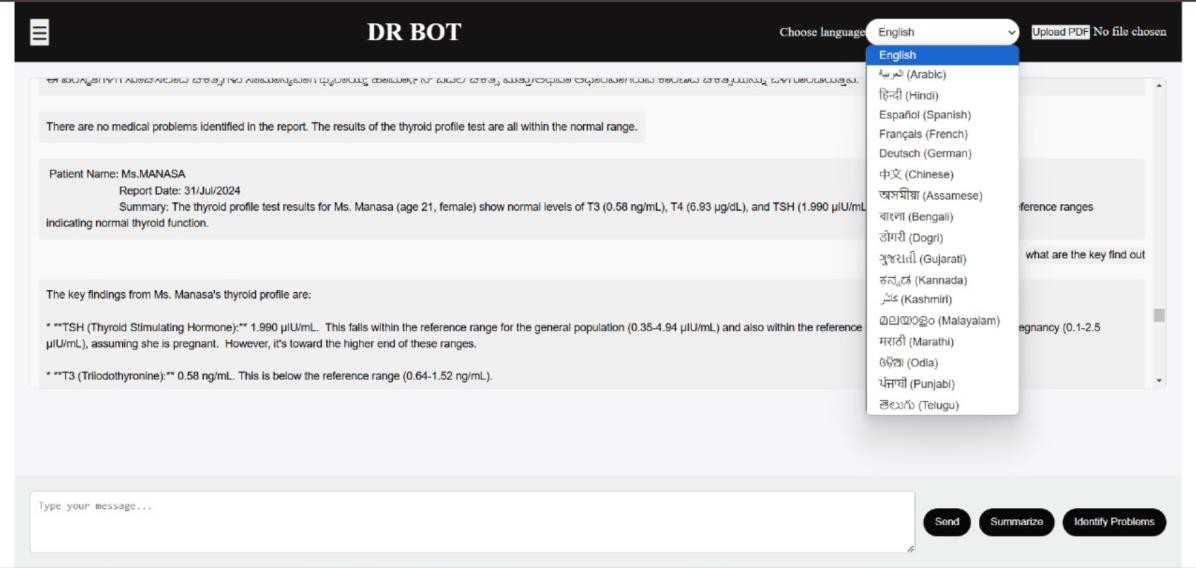 Fig1: Sign-in
Fig1: Sign-in
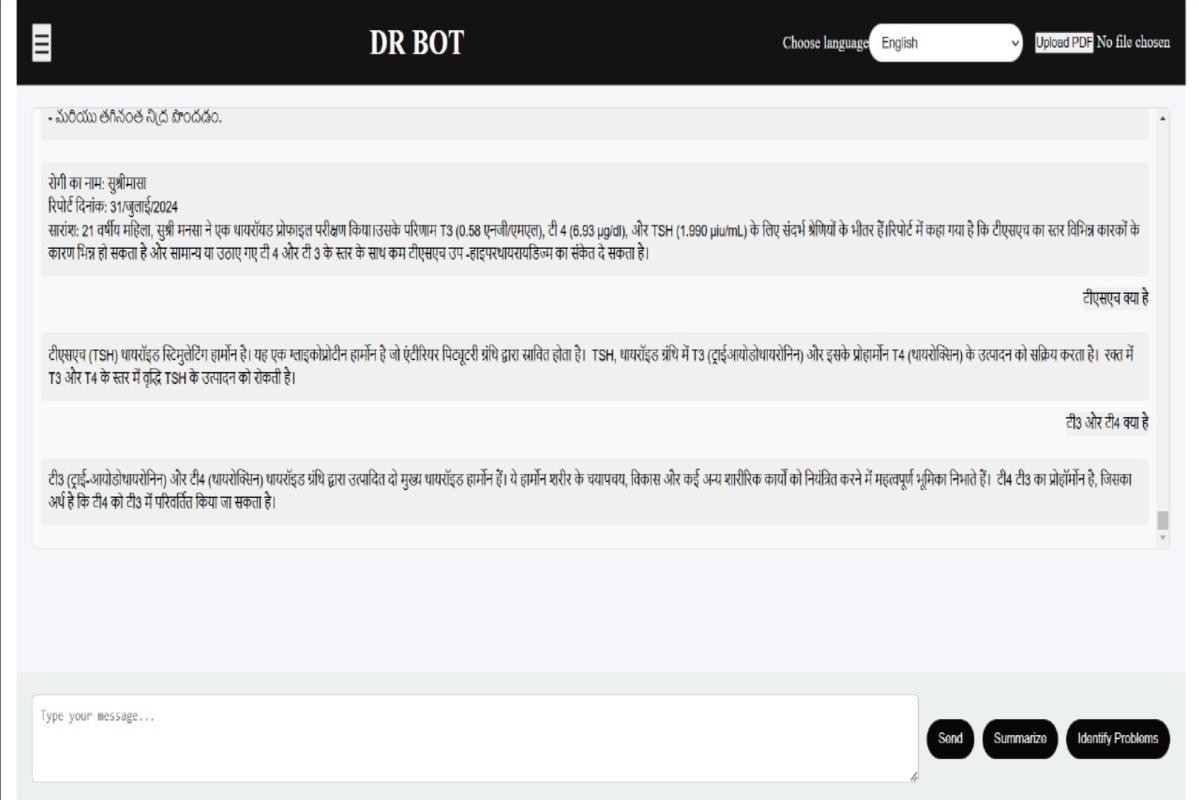 Fig2: Home
Fig2: Home
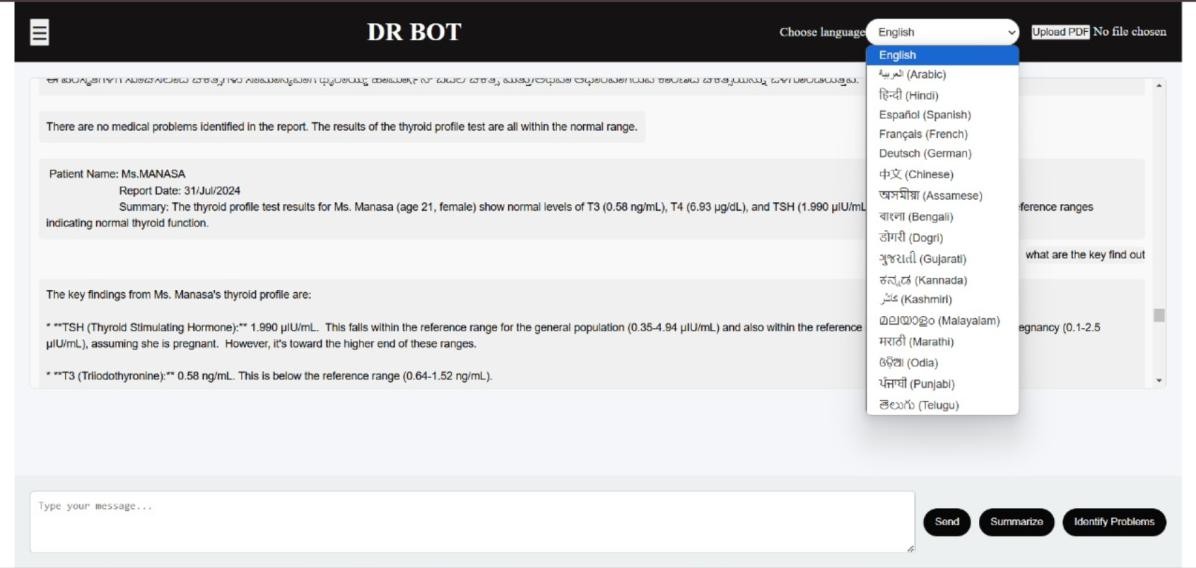 Fig3: Summary
Fig3: Summary
Conclusion
The Medical Report Summarization System is an advanced solution designed to automate the analysis and comprehension of medical data, emphasizing accessibility and precision. Powered by Bio-BERT, a natural language processing model fine-tuned on biomedical datasets, the system extracts and summarizes crucial details such as diagnoses, symptoms, and treatments from PDF- format medical reports. Key features include multilingual translation support, enabling users to access summaries and responses in their preferred language, and text-to-speech functionality, enhancing usability for individuals with reading or visual impairments. With its scalable PDF-exclusive architecture, the system ensures efficient and reliable processing of digitally generated reports, it demonstrates exceptional performance in real-world testing by improving the speed, accuracy, and accessibility of medical report handling. By integrating summarization, translation, and accessibility tools, the system empowers healthcare professionals and patients to make well-informed decisions effectively.
References
[1] M. Abu et al, “MediGPT: Exploring Potentials of Conventional and Large Language Models on Medical Data”, IEEE Access, 2024. [2] T Nadarzynski, O Miles, A Cowie, and D Ridge, “Acceptability of artificial intelligence (AI)-led chatbot services in healthcare: A mixed-methods study”, Sage Journals, 2019. [3] A Goel, Satyam, and S Sharma, “Artificial Intelligence based Healthcare Chat Bot System”, 8th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatore, India, 2023. [4] Kidwai, Bushra R K, Nadesh, “Design and Development of Diagnostic Chabot for supporting Primary Health Care Systems”, Elsevier, 2020. [5] K Jayashree, Monika K A, Preetha R., and Piraisoodan S P, “The Smart Health Care Prediction using Chatbot”, International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE), 2020. [6] M.S Bennet Praba, Sagari Sen, Chailshi Chauhan, and Divya Singh “AI Healthcare Interactive Talking Agent using NLP”, International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering (IJITEE), 2019. [7] Akshay Mendon, Megharani Patil, Yash Gupta, Vatsal Kadakia, and Hash Doshi, “Automated Healthcare System Using AI Based Chatbot”, Springer Nature Link, 2023. [8] Shahadat Uddin, Arif Khan, Md Ekramul Hossian and Mohammad Ali Moni, “Comparing different supervised machine learning algorithms for disease prediction”, Springer Nature Link, 2019. [9] G Battineni, N Chintalapudi, and F Amenta, “AI chatbot design during an epidemic like the novel coronavirus”, Healthcare, 2020. [10] S. R. Dammavalam, N. Chandana, T. R. Rao, A. Lahari, and B. Aparna, “AI Based Chatbot for Hospital Management System”, 3rd International Conference on Computing, Analytics, and Networks (ICAN), Rajpura, Punjab, India, 2022. [11] Prakhar Srivastava, Nishant Singh, “Automatized Medical Chatbot (Medibot)”, IEEE Xplore, 2020 [12] K. Srivastava, T. N. Pandey, D. Roy, and S. Sahoo, “A Machine Learning Model on Healthcare Based Chatbot and Appointment System”, 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Signal Processing (AISP), Vijayawada, India, 2023. [13] K. Anjum, M. Sameer, and S. Kumar, \"AI Enabled NLP based Text to Text Medical Chatbot,\" 2023 3rd International Conference on Innovative Practices in Technology and Management (ICIPTM), Uttar Pradesh, India, 2023. [14] P. S., N. Balakrishnan, K. T. R., A. J. B., and D. S., \"Design and Development of AI Powered Healthcare WhatsApp Chatbot,\" 2023 2nd International Conference on Vision Towards Emerging Trends in Communication and Networking Technologies (ViTECoN), Vellore, India, 2023. [15] N. A. I. Omoregbe, I. O. Ndaman, S. Misra, and O. O. Abayomi-Alli, \"Text messaging-based medical diagnosis using natural language processing and fuzzy logic,\" Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2020.
Copyright
Copyright © 2025 D Kavya, D Kiran Kumar, Divya Anjali M, Ganesh A P. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET66243
Publish Date : 2025-01-02
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

